AP计算机教程10-2:跟踪递归方法
在Java中,调用堆栈(call stack)追踪在main method执行后你所调用的所有method。栈(stack)是一种组织数据的方式,仅在栈顶添加或删除项目。日常生活中一沓杯子能很好的展示计算机科学中栈的概念。你可以从顶上取一个杯子,也可以套上更多的杯子。

当你执行method a,而它又调用了method b的时候,调用的状态会被添加到堆栈上,这样在调用完成以后能够返回到先前的位置继续执行。当method b执行完并返回后,调用的状态会从堆栈上弹出,开始恢复method a的执行环境并继续执行后续的语句。思考以下这个class定义。
public class StackTest {
public static void test1() {
System.out.println("In test1");
test2();
System.out.println("In test1 after test2");
}
public static void test2() {
System.out.println("In test2");
int y = 0;
int x = 3 / y;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("In main");
test1();
}
}
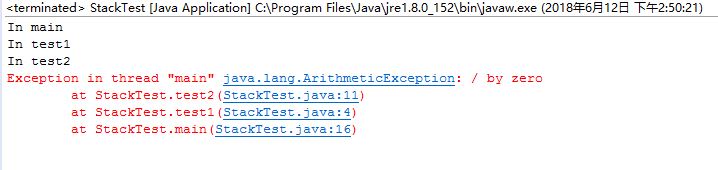
以上的代码会在执行时产生除零错。main method在第16行调用test1 method,而test1 method又在第4行调用test2 method,其在第11行产生错误。这些都可以在错误信息中看到。
当某个method调用自身时,新的调用会不断加到堆栈上。当前method的执行会暂停,以等待递归调用完成并返回。让我们来以下面的阶乘method为例说明。
public static int factorial(int n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
else
return n * factorial(n-1);
}
当调用factorial(0)时会发生什么?从代码上看会直接在第4行返回1。对于factorial(0),则会返回1 * factorial(0)。我们已经知道factorial(0)是1,但是对于计算机而言还需要重新计算。返回factorial(0)后,我们有1 * 1,最终结果为1。
因此我们可以跟踪递归的执行过程,自底而上的记下调用堆栈(即先从堆栈的底部开始写)。如果在考试中遇到计算factorial(5),草稿纸上的整个追踪过程会是这样。
factorial(5) returns 5 * factorial(4) factorial(4) returns 4 * factorial(3) factorial(3) returns 3 * factorial(2) factorial(2) returns 2 * factorial(1) factorial(1) returns 1 * factorial(0) factorial(0) returns 1
当factorial(0)执行完成之后,可以把每一步的结果代回到上一步中,模拟堆栈的弹出。这样我们又可以一步一步回到栈底(草稿纸上的顺序是从下往上)。
factorial(5) returns 5 * factorial(4) = 5 * 24 = 120 factorial(4) returns 4 * factorial(3) = 4 * 6 = 24 factorial(3) returns 3 * factorial(2) = 3 * 2 = 6 factorial(2) returns 2 * factorial(1) = 2 * 1 = 2 factorial(1) returns 1 * factorial(0) = 1 * 1 = 1 factorial(0) returns 1
因此factorial(5)的结果是120。可以使用Jeloit这一工具来查看调用堆栈。
0:00
Given the method defined below what does the following return: factorial(6)?
public static int factorial(int n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
else
return n * factorial(n-1);
}
factorial(5)再乘以6。Given the method defined below what does the following return: mystery(5)?
public static int mystery(int n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
else
return 2 * mystery (n - 1);
}
2的五次方。Given the method defined below what does the following print: mystery(4,3)?
public static int mystery(int n, int a)
{
if (n == 1) return a;
return a * mystery(n-1,a);
}
3的四次方。我们可以再看看下面bunnyEars method的执行。
public static int bunnyEars(int bunnies)
{
if (bunnies == 0) return 0;
else if (bunnies == 1) return 2;
else return 2 + bunnyEars(bunnies - 1);
}
调用bunnyEars(0)时会发生什么?从代码上看会直接在第3行返回0。bunnyEars(1)呢?,会在第4行返回2。对于bunnyEars(5),我们有:
bunnyEars(5) returns 2 + bunnyEars(4) bunnyEars(4) returns 2 + bunnyEars(3) bunnyEars(3) returns 2 + bunnyEars(2) bunnyEars(2) returns 2 + bunnyEars(1) bunnyEars(1) returns 2
重复以上的步骤,我们可以得到。
bunnyEars(5) returns 2 + bunnyEars(4) = 2 + 8 = 10 bunnyEars(4) returns 2 + bunnyEars(3) = 2 + 6 = 8 bunnyEars(3) returns 2 + bunnyEars(2) = 2 + 4 = 6 bunnyEars(2) returns 2 + bunnyEars(1) = 2 + 2 = 4 bunnyEars(1) returns 2
Given the method defined below what does the following print: mystery(1234)?
public static void mystery (int x) {
System.out.print(x % 10);
if ((x / 10) != 0) {
mystery(x / 10);
}
System.out.print(x % 10);
}
print,故是先倒序再顺序。Given the method defined below what does the following return: mystery("xyzxyxy")?
public static int mystery(String str)
{
if (str.length() == 1) return 0;
else
{
if (str.substring(0,1).equals("y")) return 1 +
mystery(str.substring(1));
else return mystery(str.substring(1));
}
}
y出现的次数,但问题在于执行到最后一个字符时就直接返回0了,因此对于所给的字符串会少算一个。
0 条评论