AP计算机教程9-4:equals method
如果没有使用extends关键字指明parent class,则class Object会被默认继承。注意到Object本身其实是有自己的field和method的,最常用到的两个会是toString()和equals()。后者用于测试当前的object和参数传入的object是否相等。
继承而来的equals method
由class Object直接继承而来的equals method仅在两个object变量存有相同的object引用时才返回true。
public class Person
{
private String name;
public Person(String theName)
{
this.name = theName;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
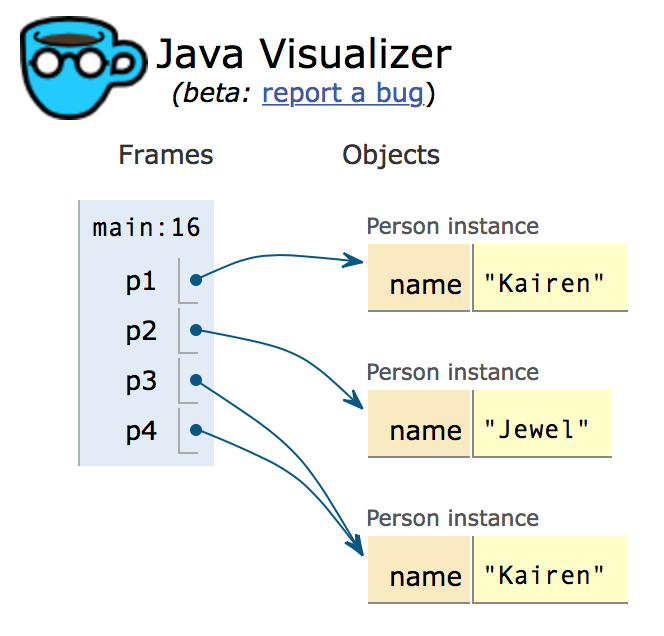
Person p1 = new Person("Kairen");
Person p2 = new Person("Jewel");
Person p3 = new Person("Kairen");
Person p4 = p3;
System.out.println(p1.equals(p2));
System.out.println(p2.equals(p3));
System.out.println(p1.equals(p3));
System.out.println(p3.equals(p4));
}
}
先推测一下结果,然后再实际执行以上代码验证看看?object引用的关系如下图所示。
String重写的equals
如果你想改变所继承的equals的工作方式,你可以重写(override)它,这样equals就会调用新写的method而不是继承的。class String就重写了equals,让两字符串长度和顺序完全一致时返回true。
public class StringTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String s1 = "hi";
String s2 = "Hi";
String s3 = new String("hi");
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println(s2.equals(s3));
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));
}
}
重写parent class中的method
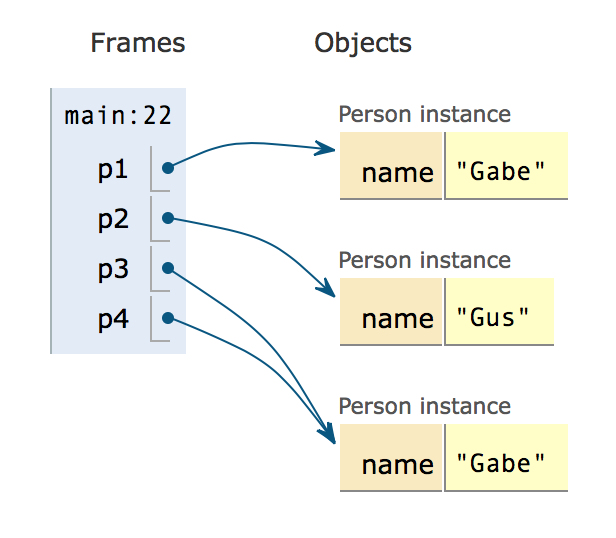
在child class中,可以通过提供同样签名的method来重写parent class中的对应method。以下的例子中,class Person也同样重写了equals。运行看看结果和第一个例子有何不同。
public class Person
{
private String name;
public Person(String theName)
{
this.name = theName;
}
public boolean equals(Object other)
{
Person otherPerson = (Person) other;
return this.name.equals(otherPerson.name);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Person p1 = new Person("Gabe");
Person p2 = new Person("Gus");
Person p3 = new Person("Gabe");
Person p4 = p3;
System.out.println(p1.equals(p2));
System.out.println(p2.equals(p3));
System.out.println(p1.equals(p3));
System.out.println(p3.equals(p4));
}
}
0 条评论