AP计算机教程6-1:Java中的数组
数组(array)是同一类型多个变量的连续存储。你可以利用索引(index),即数组中的位置,来存取变量值。数组就像超市里的存包柜一样,只是这时你无法把各种杂物塞到里面,对于给定的索引只能存储该类型变量的一个值。而索引的作用与存包柜的编号并无二致,可以帮助你找到存取东西的具体位置。想想看数组的概念还和生活中哪些常见的事物有内在联系?

当你有同种类型的数个、数十个乃至数百个数据元素需要管理但不想给它们一一命名时,数组会相当称手。在你要为游戏设计高分榜记录五个最高分和玩家的名字时,你就可以使用两个数组,一个存分数而另一个存名字。
声明数组
在声明数组时,首先明确数组中存放的元素类型,然后[]会指示这是数组而不是单纯的变量。之后再加上至少一个空格,以及最后数组的名称。注意数组的声明仅仅确定了变量的名称以及数组的类型,并没有创建数组。Java中数组同样是object,因而数组的声明只是为对应的变量引用预留了位置。如果在数组还未创建时就试图打印元素值,会得到null。可以运行以下代码验证一下。
public class Test1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// declare the arrays
int[ ] highScores = null;
String[ ] names = null;
System.out.println(highScores);
System.out.println(names);
}
}
创建数组
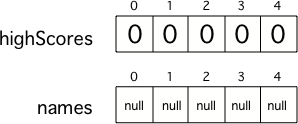
创建数组需要用到new关键字,后接空格、类型以及[]中数组的大小(能存放元素的个数)。
highScores = new int[5]; names = new String[5];
对于如double或int的数值类型,数组会初始化为0。对于boolean类型,数组会初始化为false。如String之类的object则会初始化为null。数组的索引由0开始,最后元素的索引会是数组大小/长度减一。
为数组赋值
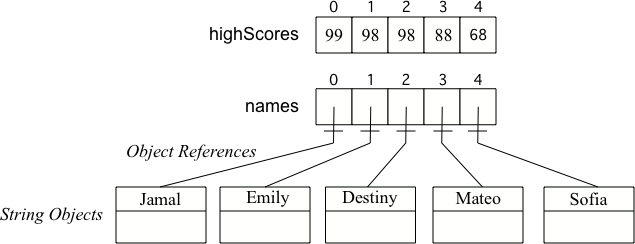
为数组赋值时,先写数组的名字加上[]包括的索引值,然后用=接上待赋值的量并用;结束语句,如highScores[0] = 99;。
public class Test1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// declare arrays
int[ ] highScores = null;
String[ ] names = null;
// create the arrays
highScores = new int[5];
names = new String[5];
// print the initial values at index 0
System.out.println(highScores[0]);
System.out.println(names[0]);
// set the values in the highScores array
highScores[0] = 99;
highScores[1] = 98;
highScores[2] = 98;
highScores[3] = 88;
highScores[4] = 68;
System.out.println(highScores[0]);
// set the values in the names array
names[0] = "Jamal";
names[1] = "Emily";
names[2] = "Destiny";
names[3] = "Mateo";
names[4] = "Sofia";
System.out.println(names[0]);
}
}
数组初始化
你还可以在创建数组的同时初始化它们(设置它们的值)。在此时你不用明确数组的大小,编译器会自动根据给定值的数目来决定。
int[ ] highScores = {99,98,98,88,68};
String[ ] names = {"Jamal", "Emily", "Destiny", "Mateo", "Sofia"};
当你创建基本变量(如int)的数组时,会依照数组元素的个数分配相应的空间并赋值。当你创建对象变量(如String)的数组时,会为object引用分配相应的空间。之后会创建每个object,并将它们的引用赋给数组让程序员可以进行后续操作。
数组长度
数组知道自身的长度(能储存多少个元素)。这是一个public的只读field,你可以使用句号标记(dot-notation)来访问它,像arrayName.length这样。句号标记指的是在变量名后加.,后接field或method的名字。注意对于数组而言,length是field而不是method,与String的length()是不同的,因而也不加()。当然如果你在考试中区分不清,也不会因此而失分。可以运行以下代码,并在之后尝试给highScore增加或减少元素,看看输出会有什么变化。
public class Test2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[ ] highScores = {99,98,98,88,68};
System.out.println(highScores.length);
}
}
0:00
What index is the first element in an array at?
0开始。Which index is the last element in an array called highScores at?
0开始,考虑仅有一个元素的数组,易见数组最后一个元素的索引是长度减一。
0 条评论