AP计算机教程4-1:条件语句
Java语句通常从上往下逐条执行。如果你希望某一语句或一段代码块仅在满足某些特定条件时执行,需要用到条件语句(conditional)。我们还使用布尔(Boolean)来形容仅取值为true或false。

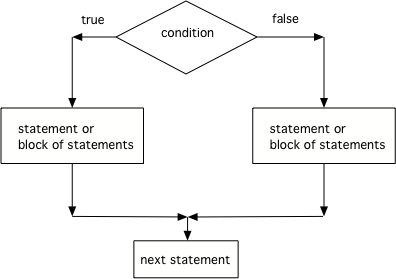
条件语句使用if关键字,后面跟着用()括起来的布尔表达式,再之后可以是一句语句也可以是用{}括起来的代码块。如果不使用{}的话,if仅作用在紧随()后的第一条语句上。如果条件为true则语句/代码块会被执行,如果条件为false则语句/代码块会被跳过。
想象一下,当即将下雨时你的手机可以自动在你离家前提醒你带上雨伞。这种情形在未来会越来越普遍,隶属于我们所说的人机交互(Human Computer Interaction, HCI)或普适计算(Ubiquitous Computing)等研究领域。以下是描述这个问题的Java代码。
public class Test1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
boolean isRaining = true;
if (isRaining) System.out.println("Take an umbrella!");
System.out.println("Drive carefully");
}
}
isRaining是一个只可以取true或false的布尔变量。如果取值为true,程序会先打印出Take an umbrella的提示,再执行后续打印Drive carefully的语句。试试看如果让isRaining取false,程序会有什么输出?
如果你想在两种可能性之间选择怎么办?当面对两难情境时,你或许会采用扔硬币解决的方式:花卉意味着一种处理方法,面额则代表另一种。对于Java编程而言,可以在if所应用到的语句或代码块后加else关键字,并随后附上另一种情况对应的语句或代码块。else对应的部分当且仅当条件为false时才会被执行。
public class Test2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
boolean isHeads = true;
if (isHeads) System.out.println("Let's go to the game");
else System.out.println("Let's watch a movie");
System.out.println("after conditional");
}
}
上述代码中,当isHeads为true时会在after conditional前打印Let's go to the game。反之先打印的则是Let's watch a movie。
以下代码无法达到预期的结果,看看可以如何修改它?
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
boolean isCold = false;
if (isCold)
System.out.println("Wear a coat");
System.out.println("Wear gloves");
System.out.println("Bye");
}
}
0:00
What is the value of grade when the following code executes and score is 93?
if (score >= 90) grade = "A"; if (score >= 80) grade = "B"; if (score >= 70) grade = "C"; if (score >= 60) grade = "D"; else grade = "E";
if语句事实上都会被执行,而grade的最终结果是最后一个if所决定的。Which of the following is equivalent to the code segment below?
if (x > 2) x = x * 2; if (x > 4) x = 0;
x变为自身的两倍以后,两个if语句条件是等价的。在都会被执行的前提下,x的最终结果是最后一个if所决定的。
0 条评论