AP计算机教程3-3:字符串相等
运算符==可以用在对象变量上,当两个变量指向同一object会返回true。对于字符串而言,这意味着将某一字符串变量赋值到另一变量中,或两个变量都已经赋为同一个字符串文本(string literal)。
以下代码演示了字符串变量间的赋值。
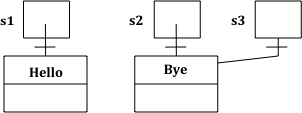
String s1 = "Hello"; String s2 = "Bye"; String s3 = s2; System.out.println(s3);
代码将会输出Bye,因为s3的值被赋为s2,它们的内容均为带有字符Bye的object引用。因为它们引用了同一object,s2==s3为true。除此之外,s2.equals(s3)也为true,因为既然是同一object,字符序列自然是完全一致的。
如果使用new关键词来创建新字符串,将会创建全新的object。因此即便创建的两个object里字符的内容和顺序完全一致,它们也会是不同的。
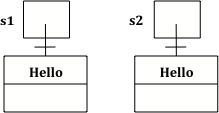
String s1 = new String("Hello");
String s2 = new String("Hello");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
两个object里的内容均为Hello。s1==s2因对象变量的引用是不同的,故而为false。但是s1.equals(s2)比较的是两个字符串的内容,会输出true。
0:00
Which of the following is true after the code executes?
String s1 = new String("hi");
String s2 = "bye";
String s3 = "hi";
s2 = s1;
注意最后一句的赋值。最后
s2与s1指向同一个object,而这个object与s3指向的object不同,但字符串内容相等。2
0 条评论